File Explorer is the backbone of navigating files and folders on any Windows 11 system. When it stops working properly or becomes confusing to use, productivity grinds to a halt. This guide walks through the most effective solutions to get help with File Explorer in Windows 11, from basic troubleshooting to advanced fixes that restore full functionality.
Understanding File Explorer Issues in Windows 11
Most people find that File Explorer problems fall into a few common categories. The application might crash frequently, freeze when opening folders, fail to display files correctly, or refuse to launch altogether. Sometimes the Quick Access section stops updating, or search functionality becomes unreliable. These issues can stem from corrupted system files, outdated software, conflicting third-party programs, or simple configuration errors.
The key is to identify the specific symptom before attempting fixes. A crashing File Explorer requires different solutions than one that simply runs slowly. Taking a moment to note exactly what goes wrong—and when—saves time in the troubleshooting process.
Quick Fixes That Solve Most File Explorer Problems
Before diving into complex solutions, these simple steps resolve the majority of File Explorer issues:
Restart File Explorer Process
This works best when File Explorer becomes unresponsive or displays content incorrectly. The process takes less than a minute:
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager, or right-click the Windows icon and select Task Manager.
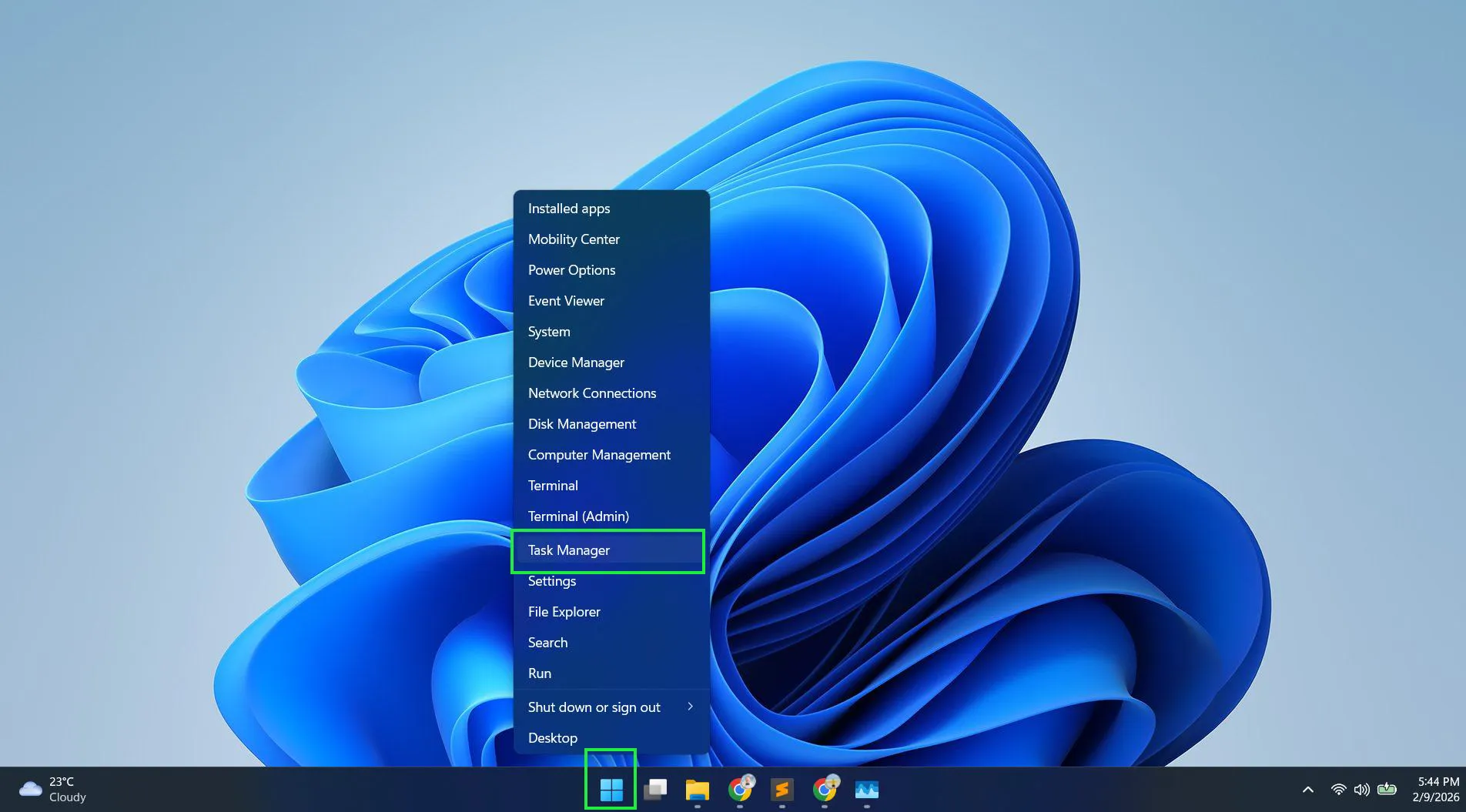
- Locate ‘Windows Explorer’ in the Processes tab
- Right-click on Windows Explorer and select ‘Restart’
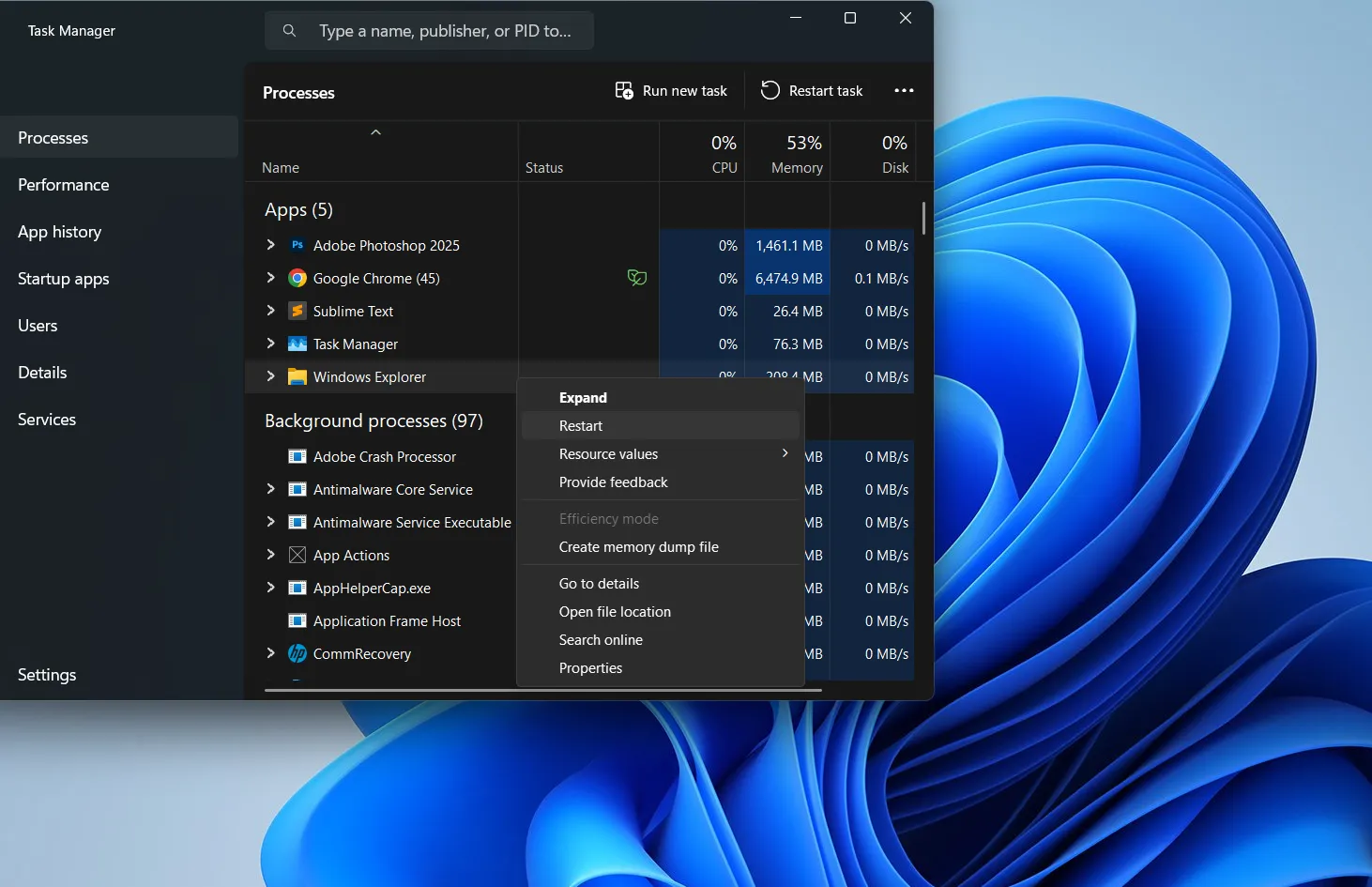
- Wait a few seconds while the process restarts automatically
Watch this: Easy Way to Restart File Explorer Process
The desktop and taskbar will briefly disappear before reappearing. This simple restart clears temporary glitches without affecting open documents or applications.
Clear File Explorer History
Accumulated history data sometimes causes sluggish performance or display errors. Clearing this data often restores normal operation:
- Open File Explorer and click the three-dot menu icon
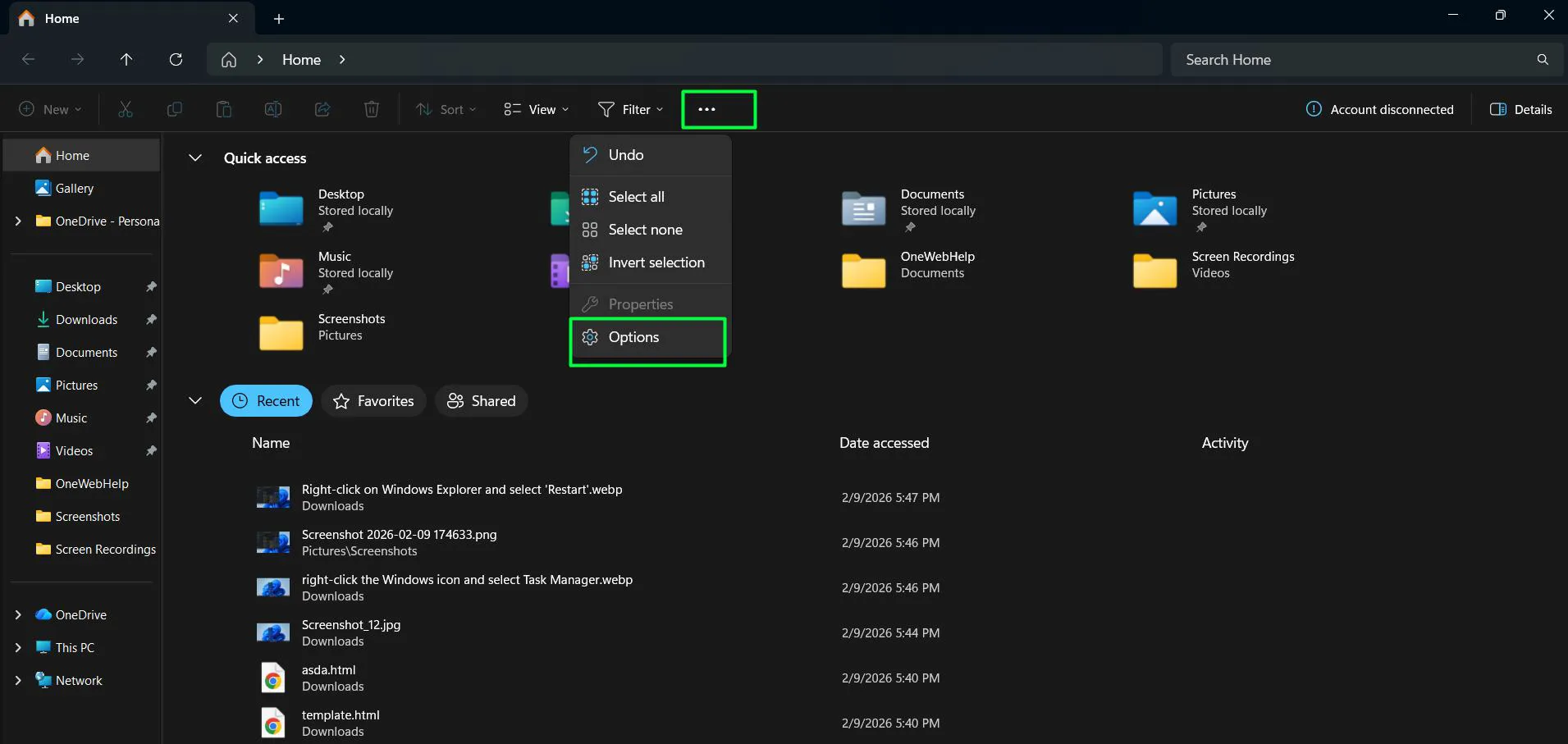
- Select ‘Options’ to open Folder Options
- Under the General tab, find the Privacy section
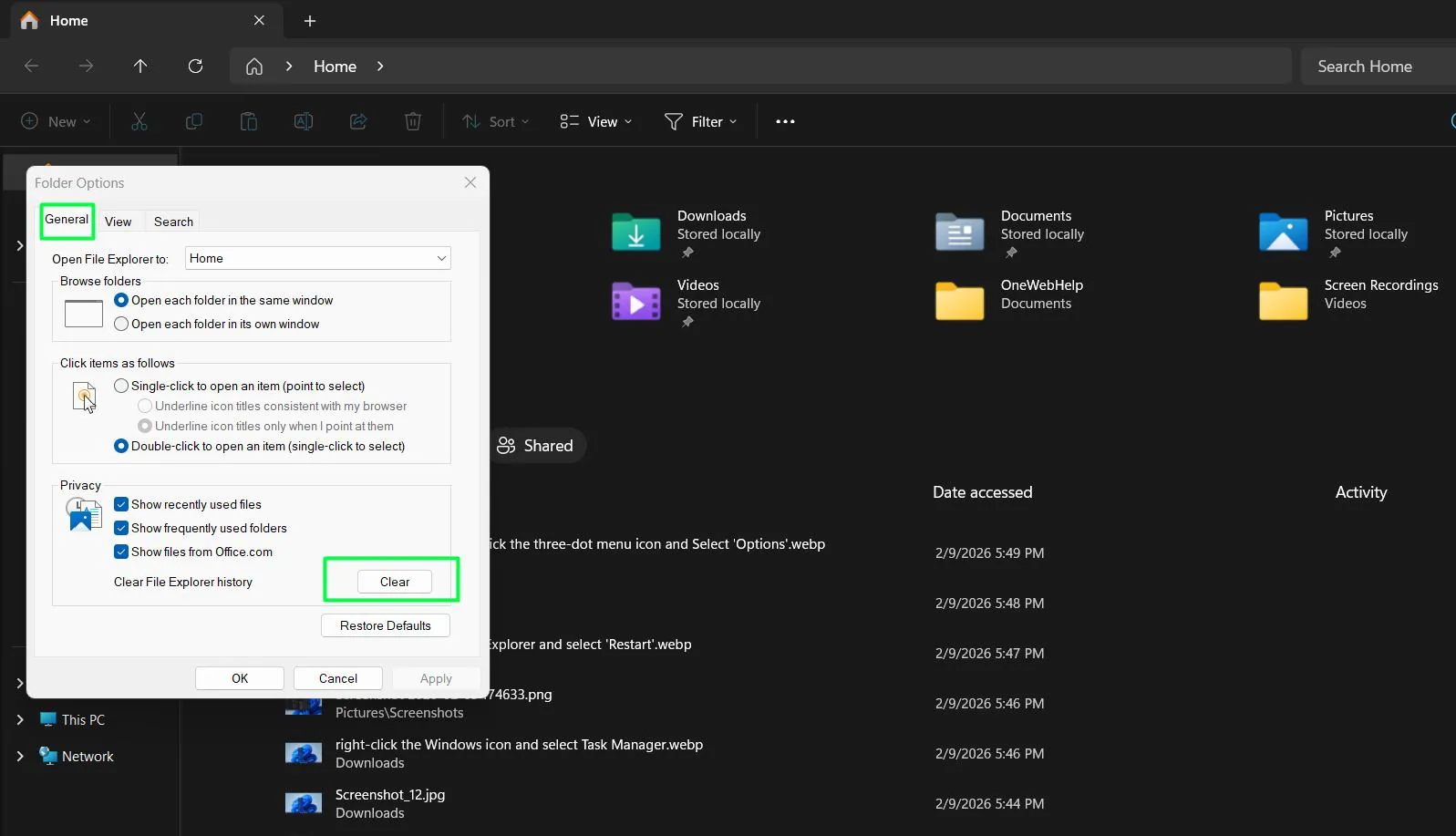
- Click ‘Clear’ next to ‘Clear File Explorer history’
- Click ‘OK’ to apply changes
Advanced Troubleshooting for Persistent Issues
When quick fixes don’t resolve the problem, these more comprehensive solutions address deeper system issues.
Run System File Checker
Corrupted system files frequently cause File Explorer malfunctions. The built-in System File Checker scans and repairs these files automatically. Most people find this tool eliminates problems that seemed unsolvable:
- Right-click the Start button and select ‘Terminal (Admin)’
- Type the command: sfc /scannow
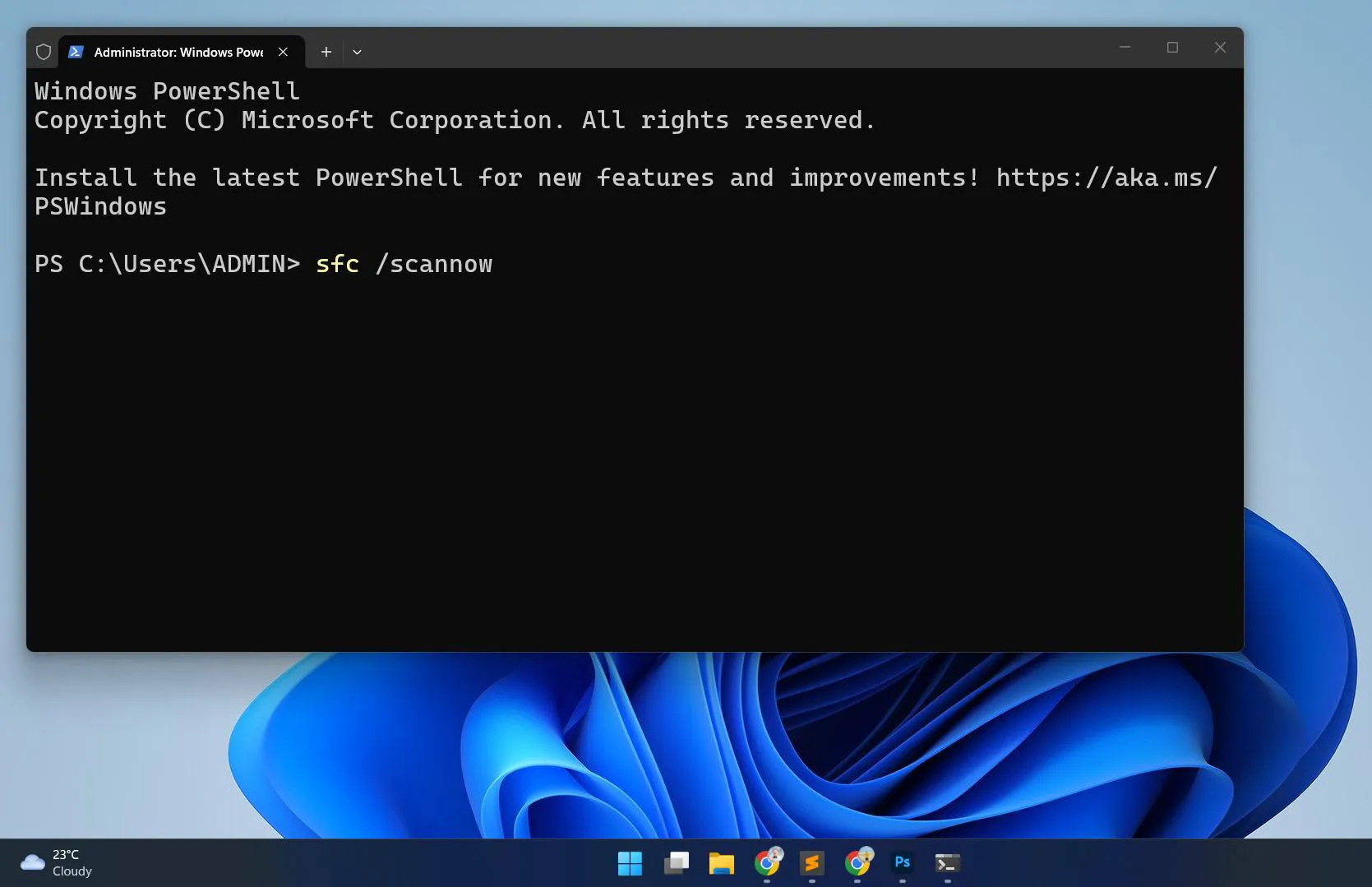
- Press Enter and wait while the scan completes (this takes 15-30 minutes)
- Restart the computer after the scan finishes
The scan examines every protected system file and replaces corrupted versions with cached copies. This process runs entirely in the background and doesn’t require additional input.
Use DISM Tool to Repair Windows Image
When System File Checker finds problems it can’t fix, the Deployment Image Servicing and Management tool provides a deeper repair option:
- Right-click the Start button and select ‘Terminal (Admin)’
- Type: DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth
- Press Enter and allow 20-40 minutes for completion
- Run the sfc /scannow command again after DISM finishes
- Restart the system
DISM connects to Windows Update servers to download replacement files for damaged components. A stable internet connection ensures the process completes successfully.
Reset File Explorer Settings
Sometimes custom settings or corrupted preferences cause unexpected behavior. Resetting File Explorer to default settings provides a fresh start:
- Open File Explorer and click the three-dot menu
- Select ‘Options’ to access Folder Options
- Click the ‘Restore Defaults’ button under each tab (General, View, Search)
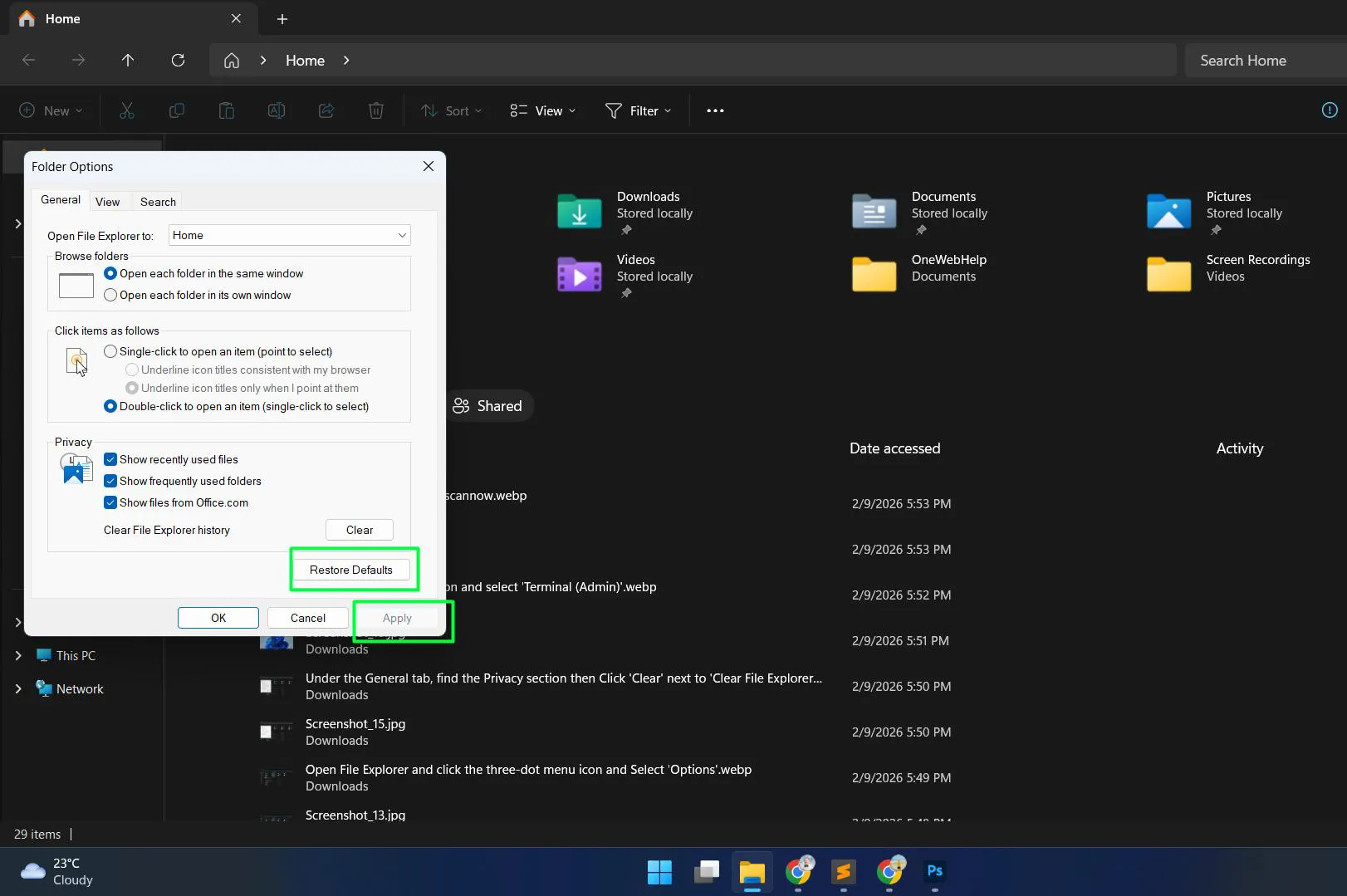
- Apply the changes and restart File Explorer
This action doesn’t delete files or folders—it only resets how File Explorer displays and organizes content.
Optimizing File Explorer Performance
Beyond fixing problems, certain adjustments improve File Explorer speed and responsiveness on Windows 11 systems.
Disable Home or Quick Access
Quick Access tracks recently used files and folders, but this feature sometimes slows down File Explorer, especially on systems with limited hardware resources:
- Open File Explorer Options from the three-dot menu
- Under the General tab, change ‘Open File Explorer to’ from ‘Home’ to ‘This PC’
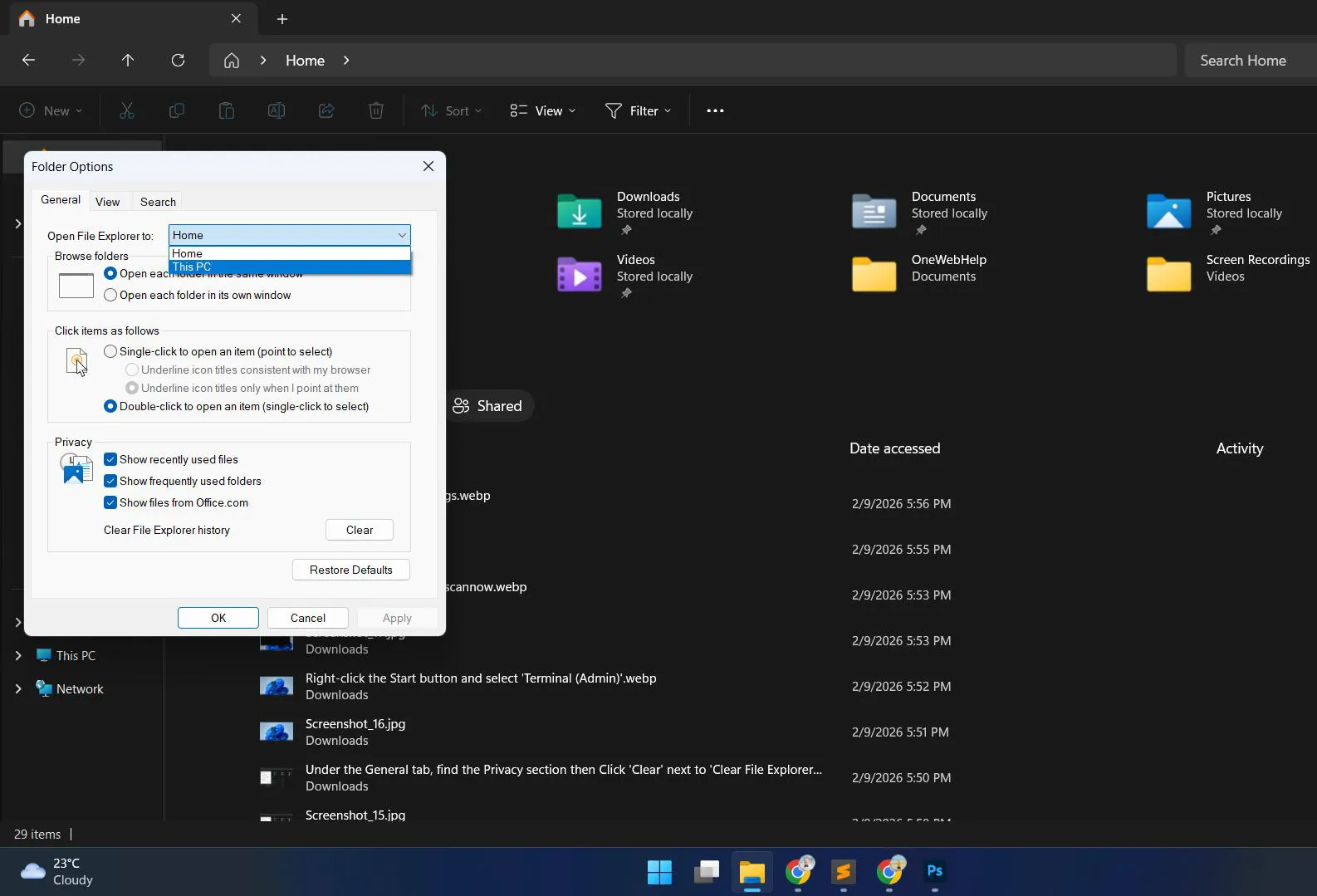
- Uncheck ‘Show recently used files’ and ‘Show frequently used folders’
- Click ‘OK’ to save changes
Adjust View Settings for Better Performance
Thumbnail generation and preview features consume system resources. Disabling these options speeds up folder navigation:
- Open Folder Options and switch to the View tab
- Check ‘Always show icons, never thumbnails’
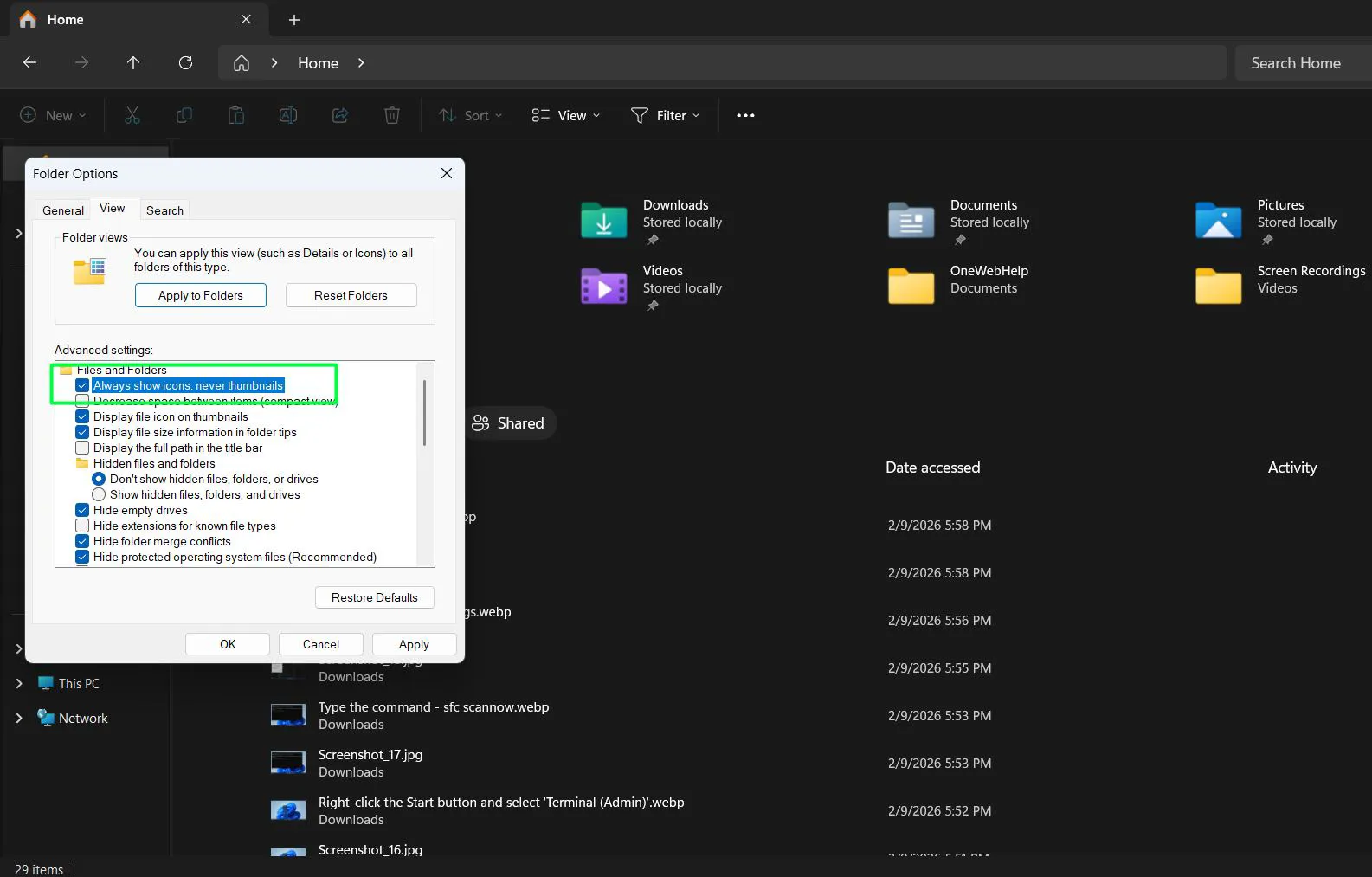
- Uncheck ‘Show preview handlers in preview pane’
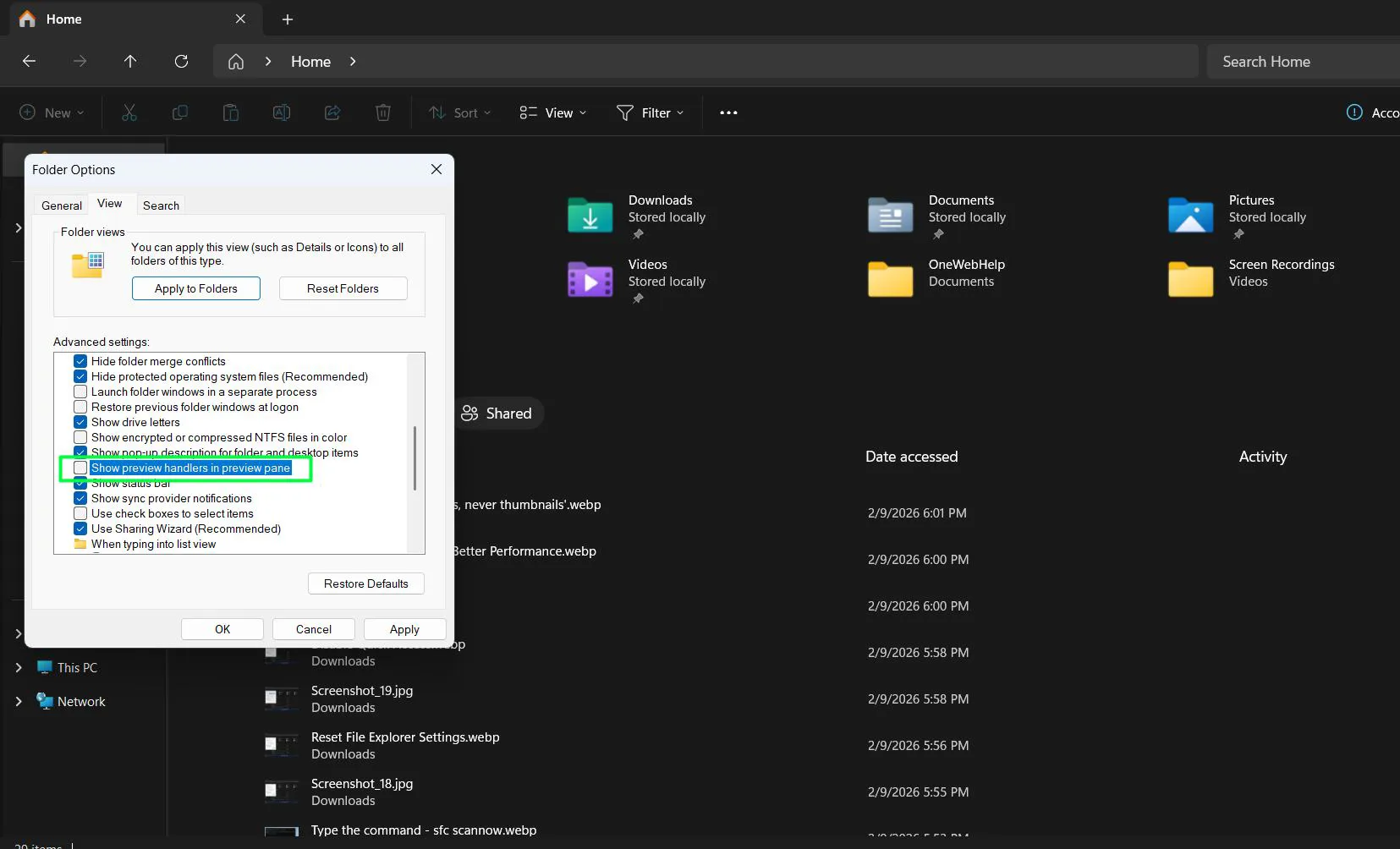
- Apply settings and test performance
Folders containing thousands of files open noticeably faster with these adjustments, though the visual presentation becomes more basic.
Fixing Specific File Explorer Features
Different components of File Explorer may require targeted solutions when they malfunction independently.
Repair Search Functionality
When File Explorer search returns incomplete results or fails entirely, rebuilding the search index typically solves the issue:
- Type ‘Indexing Options’ in the Windows search box and open it
- Click the ‘Advanced’ button in the Indexing Options window
- Under the Index Settings tab, click ‘Rebuild’
- Confirm the action and wait several hours for completion
The rebuild process runs in the background and won’t interfere with normal computer use, though initial searches may be slower until indexing completes.
Restore Missing Toolbar Icons
Sometimes the File Explorer toolbar appears blank or missing icons. This works best when resolved through a simple settings reset:
- Open File Explorer and click View in the toolbar
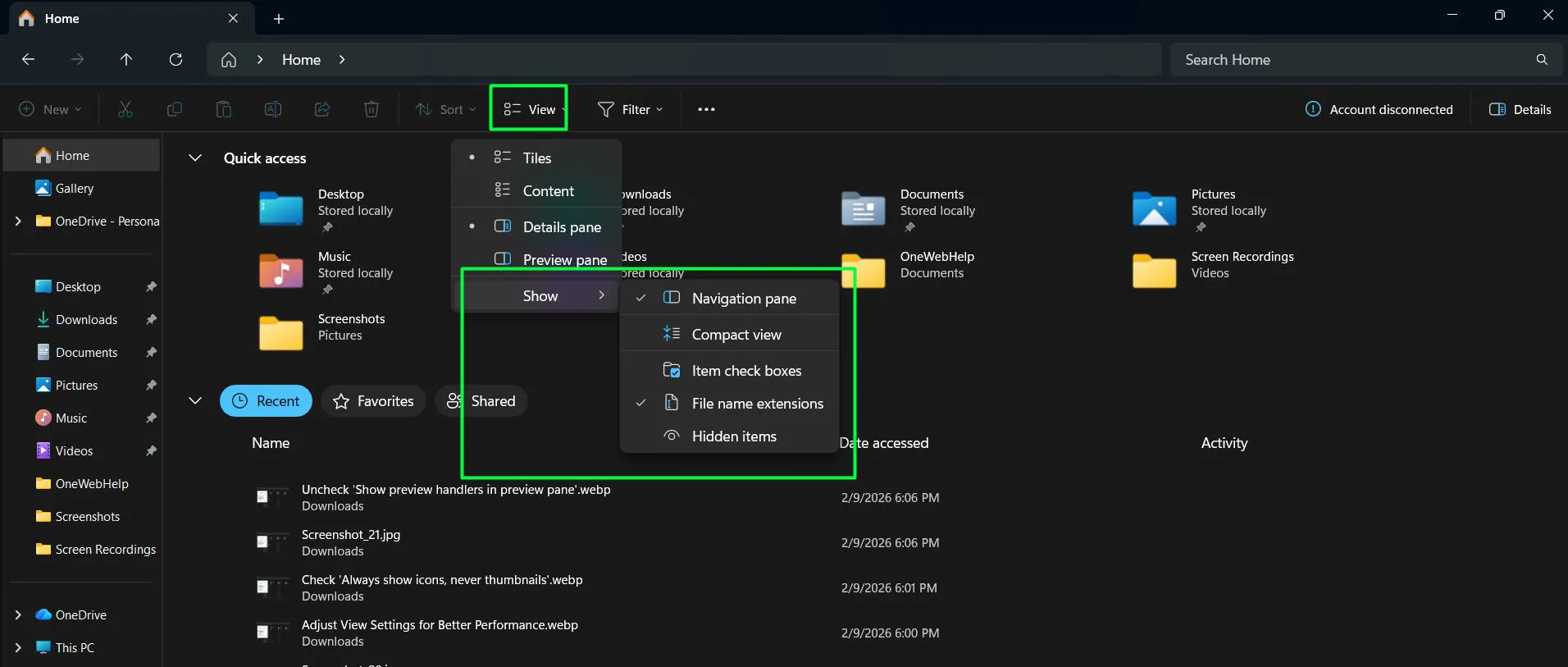
- Select ‘Show’ and ensure all desired elements are checked
- If icons remain missing, restart File Explorer through Task Manager
- Consider running System File Checker if the problem persists
Using Windows Troubleshooter for Automated Help
Windows 11 includes built-in troubleshooters that automatically detect and fix common File Explorer problems. These tools work best for users who prefer automated solutions:
- Press Windows + I to open Settings
- Navigate to System, then Troubleshoot
- Click ‘Other troubleshooters’
- Find and run the ‘Windows Store Apps’ troubleshooter (File Explorer is technically an app)
- Follow on-screen instructions and apply recommended fixes
The troubleshooter scans for issues with permissions, corrupted files, and configuration errors, then attempts automatic repairs. Success rates vary, but the process requires minimal technical knowledge.
Creating a New User Profile to Isolate Issues
Occasionally, File Explorer problems stem from a corrupted user profile rather than system-wide issues. Creating a new user account helps identify whether this is the case:
- Open Settings and go to Accounts
- Select ‘Family & other users’
- Click ‘Add account’ under Other users
- Follow prompts to create a new local account
- Sign out and log in to the new account
- Test File Explorer functionality
If File Explorer works perfectly in the new account, the original profile contains the problem. Transferring files to the new account and using it as the primary profile resolves the issue permanently.
Preventing Future File Explorer Problems
Regular maintenance reduces the likelihood of encountering File Explorer issues. These preventive measures keep the system running smoothly:
Keep Windows 11 updated with the latest patches and feature updates. Microsoft regularly releases fixes for known File Explorer bugs. Enable automatic updates or check manually each month to ensure the system receives these improvements.
Avoid installing questionable third-party shell extensions or file management tools. These programs integrate deeply with File Explorer and often cause conflicts. Stick to reputable software from trusted developers.
Run Disk Cleanup monthly to remove temporary files and clear system caches. Accumulated junk files sometimes interfere with File Explorer operations. The built-in Disk Cleanup tool safely removes unnecessary data.
Perform regular malware scans using Windows Security or a trusted third-party antivirus. Malware infections occasionally target File Explorer to hide their presence or disrupt system operations.
When to Consider Professional Help
Some File Explorer problems indicate deeper hardware or software issues beyond typical troubleshooting. Persistent crashes after trying all solutions, File Explorer problems accompanied by widespread system instability, or situations where multiple Windows components malfunction simultaneously suggest more serious underlying problems.
In these cases, backing up important data and considering a clean Windows installation might be necessary. Professional technical support can also diagnose hardware failures or complex software conflicts that aren’t easily resolved through standard troubleshooting.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why does File Explorer keep crashing in Windows 11?
File Explorer crashes typically result from corrupted system files, conflicting third-party software, outdated graphics drivers, or damaged user profiles. Running System File Checker and updating all drivers resolves most crashing issues. If crashes persist, creating a new user profile often eliminates profile-specific corruption.
How do I reset File Explorer to default settings?
Open File Explorer, click the three-dot menu, select Options, then click Restore Defaults under each tab in Folder Options. This resets view preferences, search settings, and general behavior without deleting any files. Restart File Explorer through Task Manager after applying changes for them to take full effect.
Can I reinstall File Explorer in Windows 11?
File Explorer is a core Windows component that cannot be traditionally uninstalled or reinstalled like regular applications. However, running System File Checker (sfc /scannow) and DISM repair commands effectively repairs or replaces damaged File Explorer files. A clean Windows installation provides the only true reinstallation option.
Why is File Explorer so slow in Windows 11?
Slow File Explorer performance usually stems from Quick Access tracking, thumbnail generation for large folders, indexing operations, or insufficient system resources. Disable Quick Access, turn off thumbnail previews, exclude certain folders from indexing, and ensure adequate RAM availability. Disk fragmentation on older hard drives also causes slowdowns.
How do I access File Explorer help in Windows 11?
Press F1 while File Explorer is active to open Windows Help. Alternatively, click the three-dot menu in File Explorer and select Help. Microsoft’s support website provides comprehensive documentation, and the Get Help app in Windows 11 offers troubleshooting assistance with interactive guides and chat support options.
What should I do if File Explorer won’t open at all?
If File Explorer refuses to launch, press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager, click File, select Run new task, type ‘explorer.exe’, and press Enter. If this fails, boot into Safe Mode and run System File Checker and DISM repair commands. Severe cases may require system restore to a previous working state.
