Managing power and sleep settings in Windows 11 can significantly impact battery life, energy consumption, and overall system performance. The process is straightforward once the right settings are located. This guide walks through the exact steps to adjust when the screen turns off and when the computer goes to sleep.
Understanding Power and Sleep Settings
Windows 11 provides granular control over when displays turn off and when the system enters sleep mode. These settings differ based on whether the device is plugged in or running on battery power. Most laptops benefit from aggressive sleep timers on battery, while desktops typically use longer intervals or disable sleep entirely.
The power settings affect two main functions: screen timeout and system sleep. Screen timeout simply turns off the display while keeping the system active, whereas sleep mode puts the entire computer into a low-power state. Think of it like the difference between closing your eyes and actually going to sleep.
Accessing Power and Sleep Settings Through Settings App
The Settings app provides the most user-friendly way to change power and sleep settings in Windows 11. Here’s how to get there:
- Click the Start button or press the Windows key on the keyboard
- Select ‘Settings’ from the pinned apps or type ‘settings’ in the search box
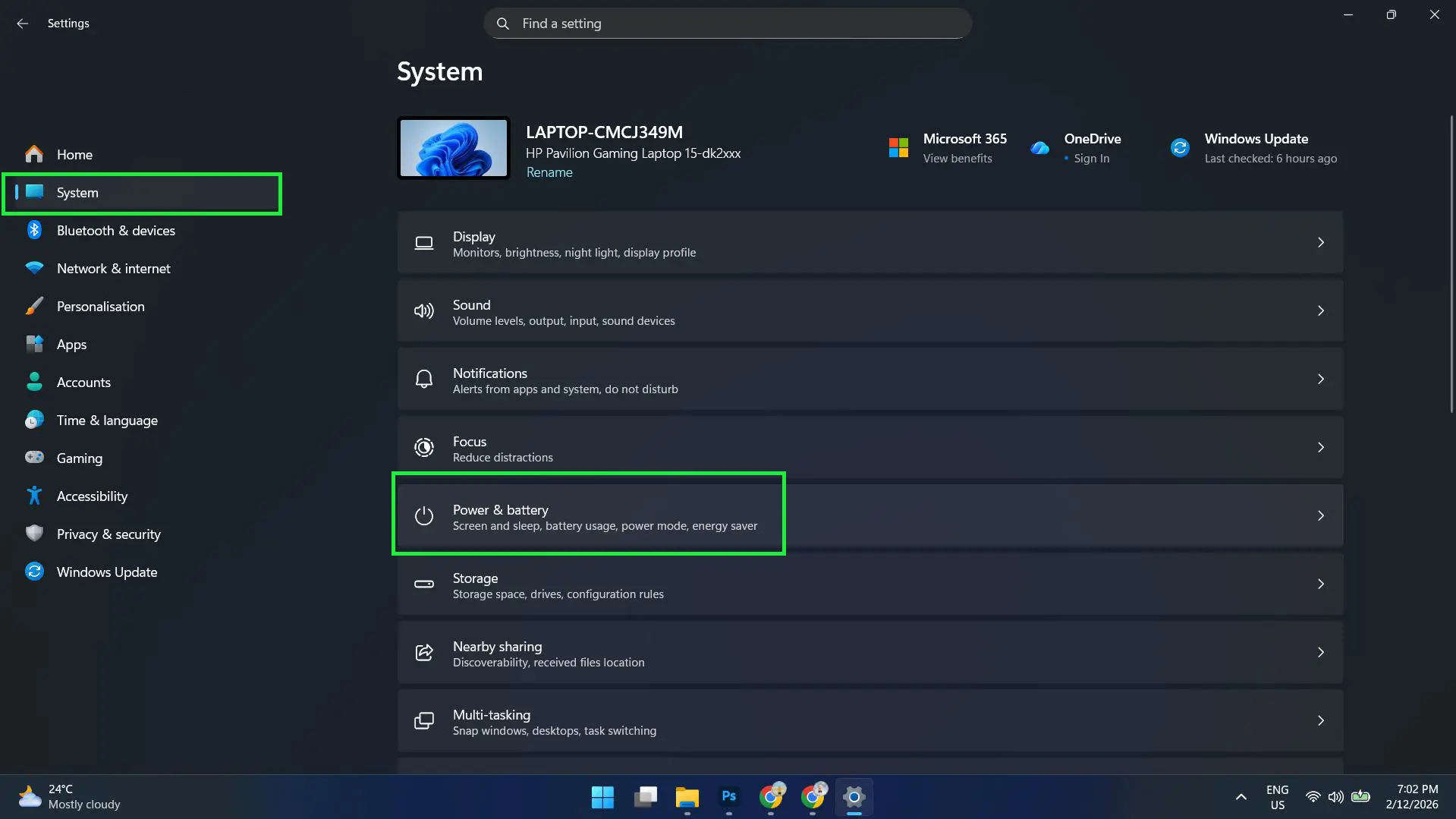
- Click on ‘System’ in the left sidebar
- Select ‘Power & battery’ from the System options
- Look for the ‘Screen, sleep, & hibernate time-outs’ section and click to expand it
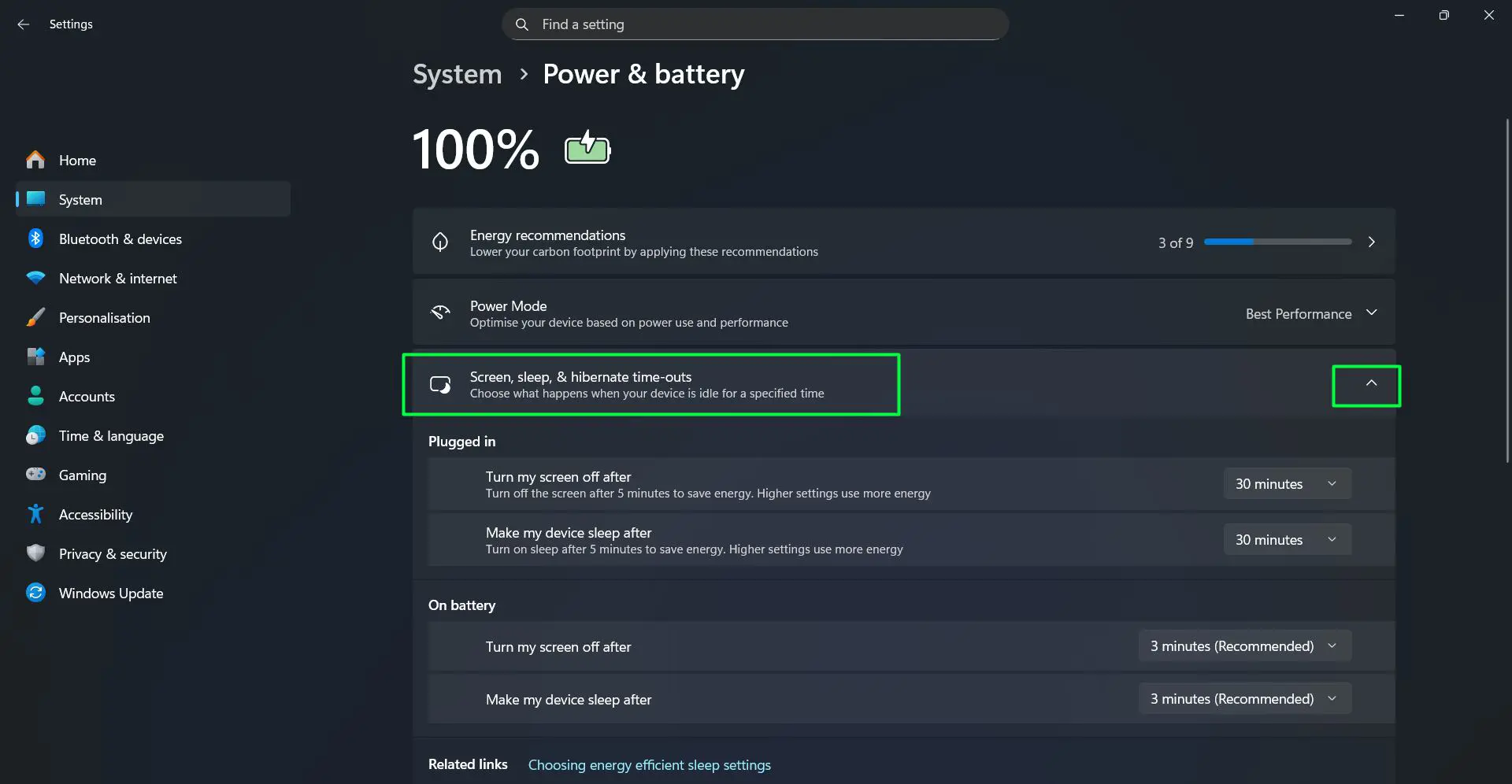
This works best when the Settings app is already pinned to the taskbar for quick access. Alternatively, pressing Windows + I opens Settings directly, saving a few clicks.
Watch this: How to Change Power and Sleep Settings in Windows 11 Easily
Adjusting Screen Timeout Settings
The screen timeout determines how long the display stays on during inactivity. Different scenarios call for different settings. Windows 11 displays these options under ‘Screen, sleep, & hibernate time-outs’ with separate controls for plugged in and battery modes.
For Plugged In Power
Under ‘Plugged in’, find the ‘Turn my screen off after’ dropdown menu and select the preferred time interval. Options range from 1 minute to never. Most people find that 30 minutes works well for desktop computers, while those who frequently step away might prefer 10 or 15 minutes.
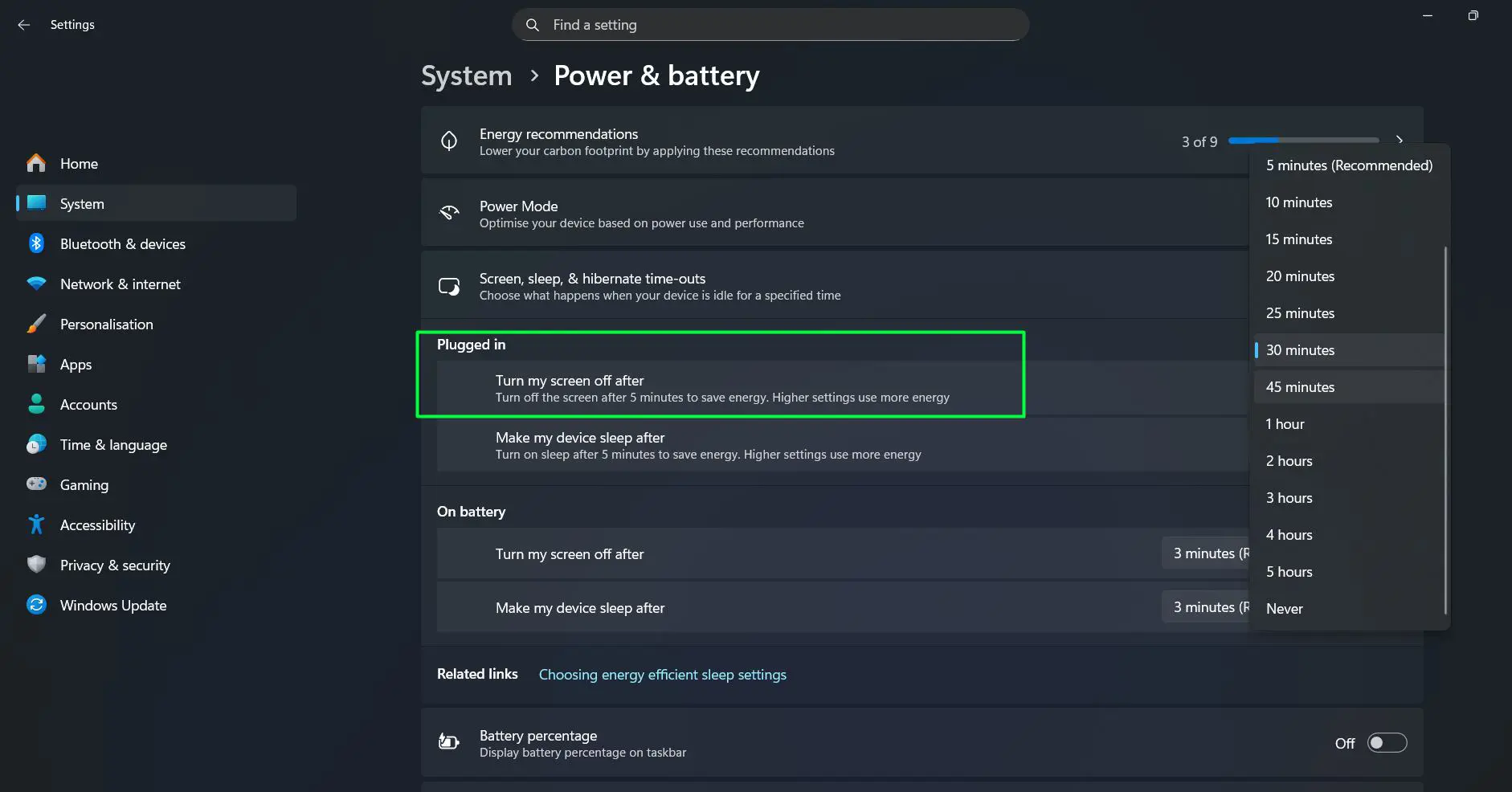
The description reads ‘Turn off the screen 5 minutes to save energy. Higher settings use more energy’, reminding users of the energy implications. Desktop users often set this to longer periods since energy consumption isn’t as critical as with laptops.
For Battery Power
The ‘On battery’ section contains the ‘Turn my screen off after’ setting for when the laptop is unplugged. Shorter intervals between 3 to 5 minutes help conserve battery life. Windows 11 often recommends 3 minutes as an optimal setting, marked with ‘(Recommended)’ next to the time value.
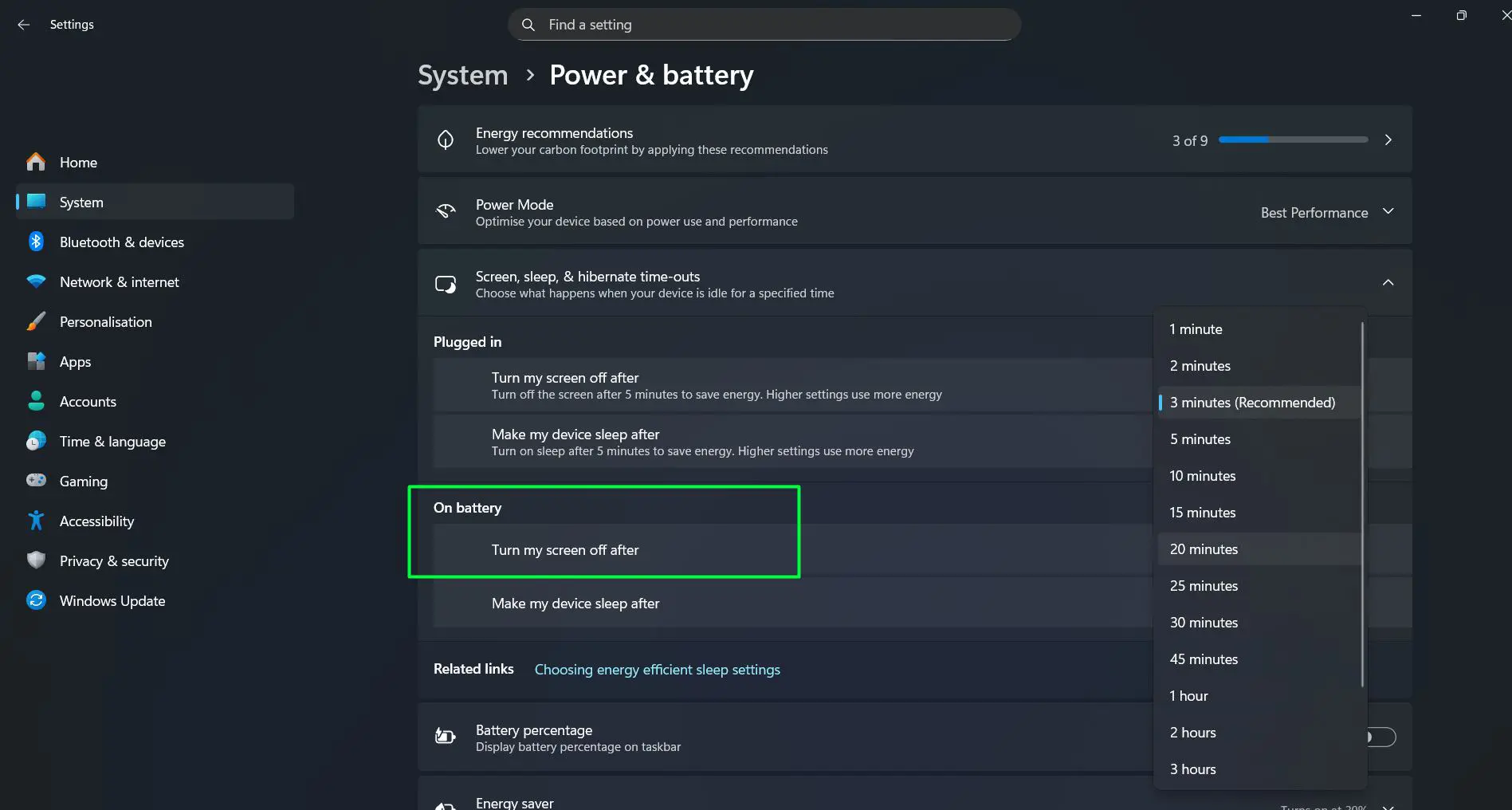
Pro-Tip: The recommended settings in Windows 11 are based on energy efficiency data from thousands of devices. Following these recommendations typically provides the best balance between usability and battery conservation for most users.
Configuring Sleep Timer Settings
Sleep settings determine when the entire system enters a low-power state. This affects running applications and network connectivity. The settings appear directly below the screen timeout options in the same expandable section.
Plugged In Sleep Settings
Navigate to the ‘Plugged in’ section and find ‘Make my device sleep after’. Choose an appropriate interval from the dropdown menu. Common choices include 30 minutes, 1 hour, or 2 hours for desktop computers. The key is to choose a duration that won’t interrupt active work sessions but still provides some power savings during extended breaks.
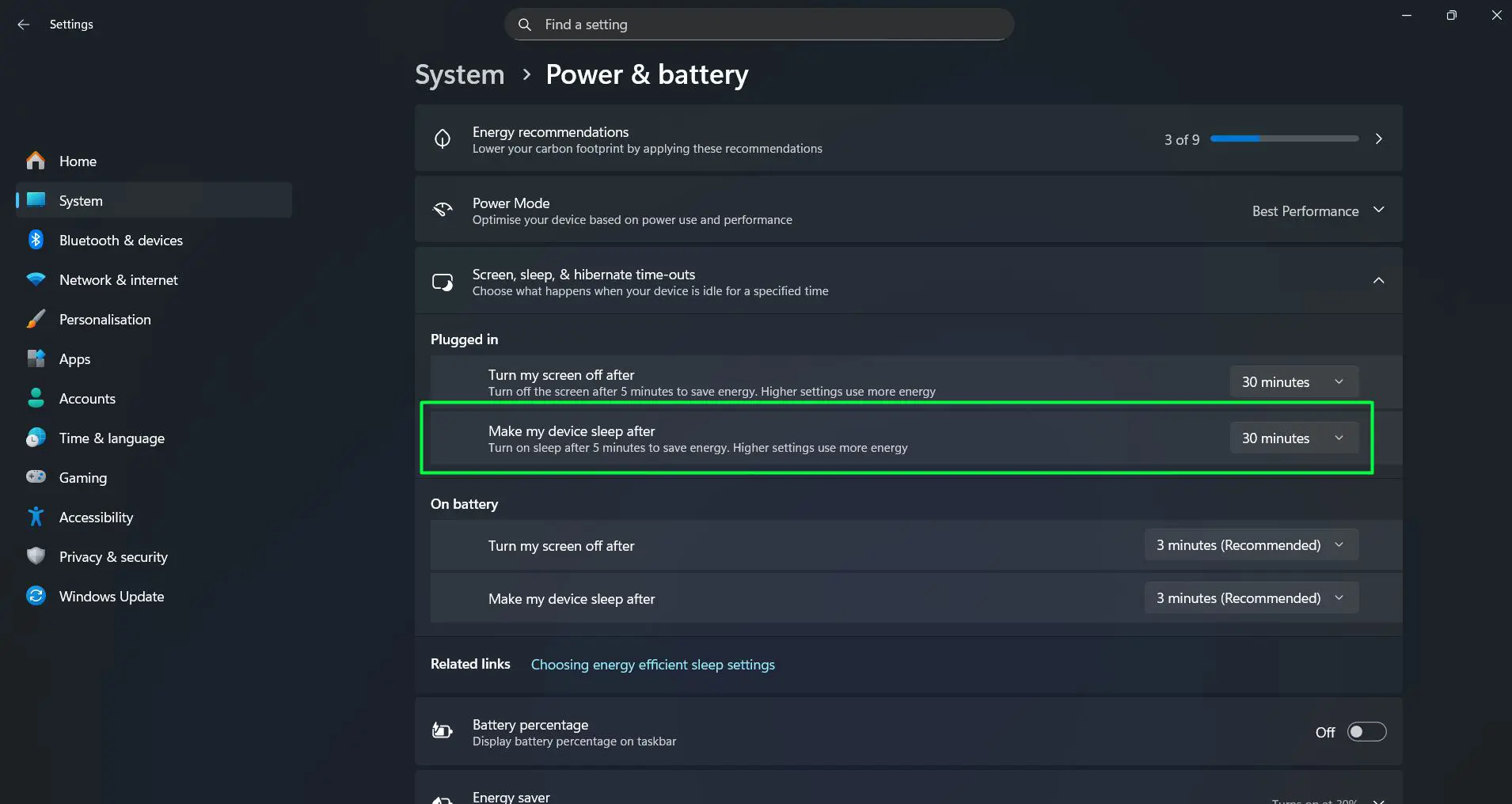
Battery Sleep Settings
Under ‘On battery’, the ‘Make my device sleep after’ option controls sleep behavior when running on battery power. Shorter times between 5 to 15 minutes maximize battery life on laptops. Windows 11 typically recommends 3 minutes, matching the screen timeout recommendation for optimal battery preservation.
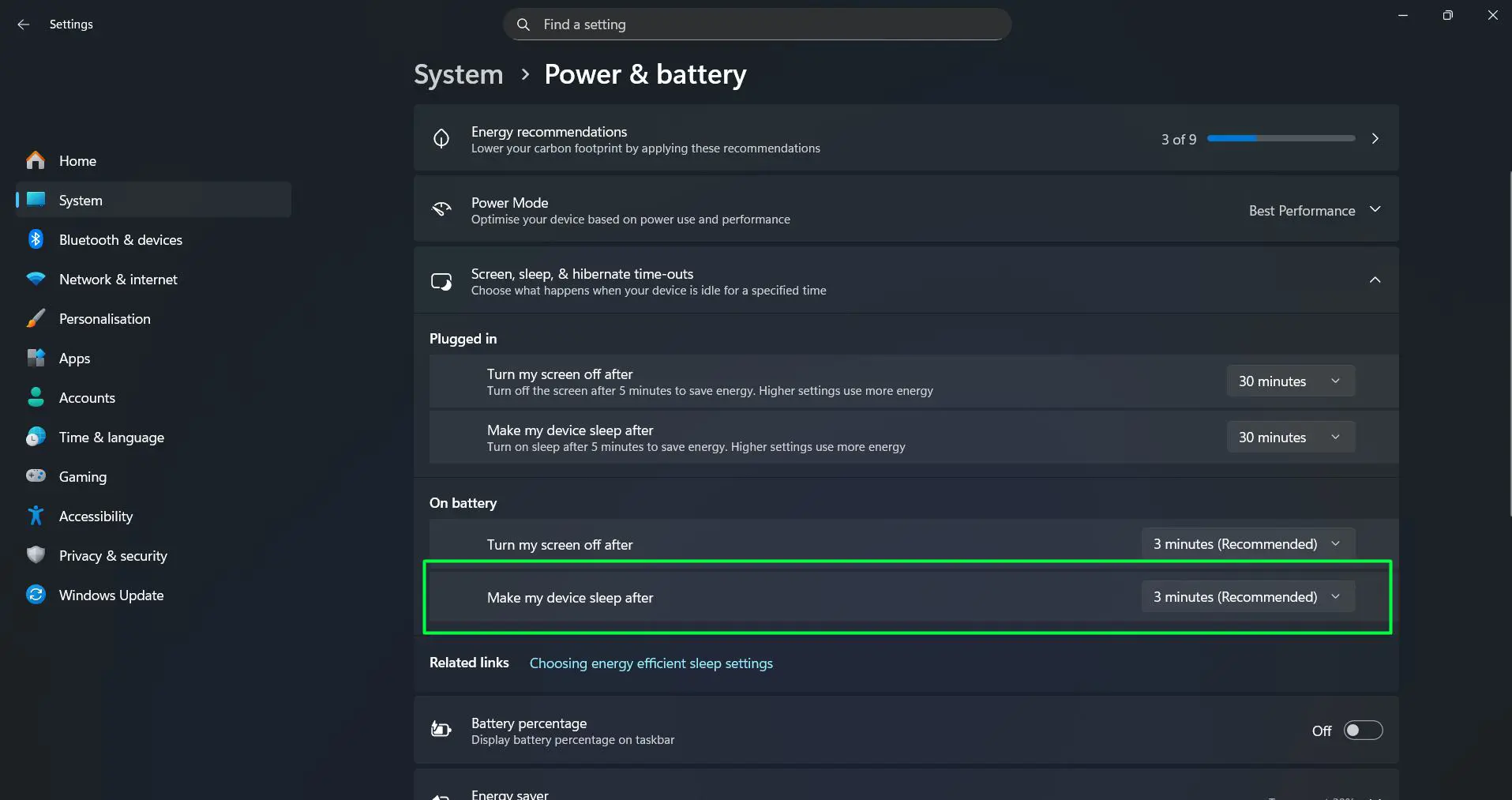
The description ‘Turn on sleep after 5 minutes to save energy. Higher settings use more energy’ appears below each setting, providing immediate feedback about energy consumption choices.
Using Quick Settings to Access Power Mode Settings
Windows 11 includes a quick power mode selector accessible from the system tray that affects performance and battery usage:
- Click the battery icon in the system tray (bottom-right corner of the screen)
- The Quick Settings panel opens showing network, Bluetooth, and other toggles
- Look at the bottom section where you can see the battery percentage icon and click it
- Access power mode options through the battery settings
Quick Settings also displays the current battery percentage and charging status. The Energy saver toggle appears in the Quick Settings panel, allowing rapid activation of power-saving features with a single click.
Understanding Power Mode Options
The Power Mode setting in the Power & battery page allows optimization of device performance based on current needs. The description reads ‘Optimise your device based on power use and performance’.
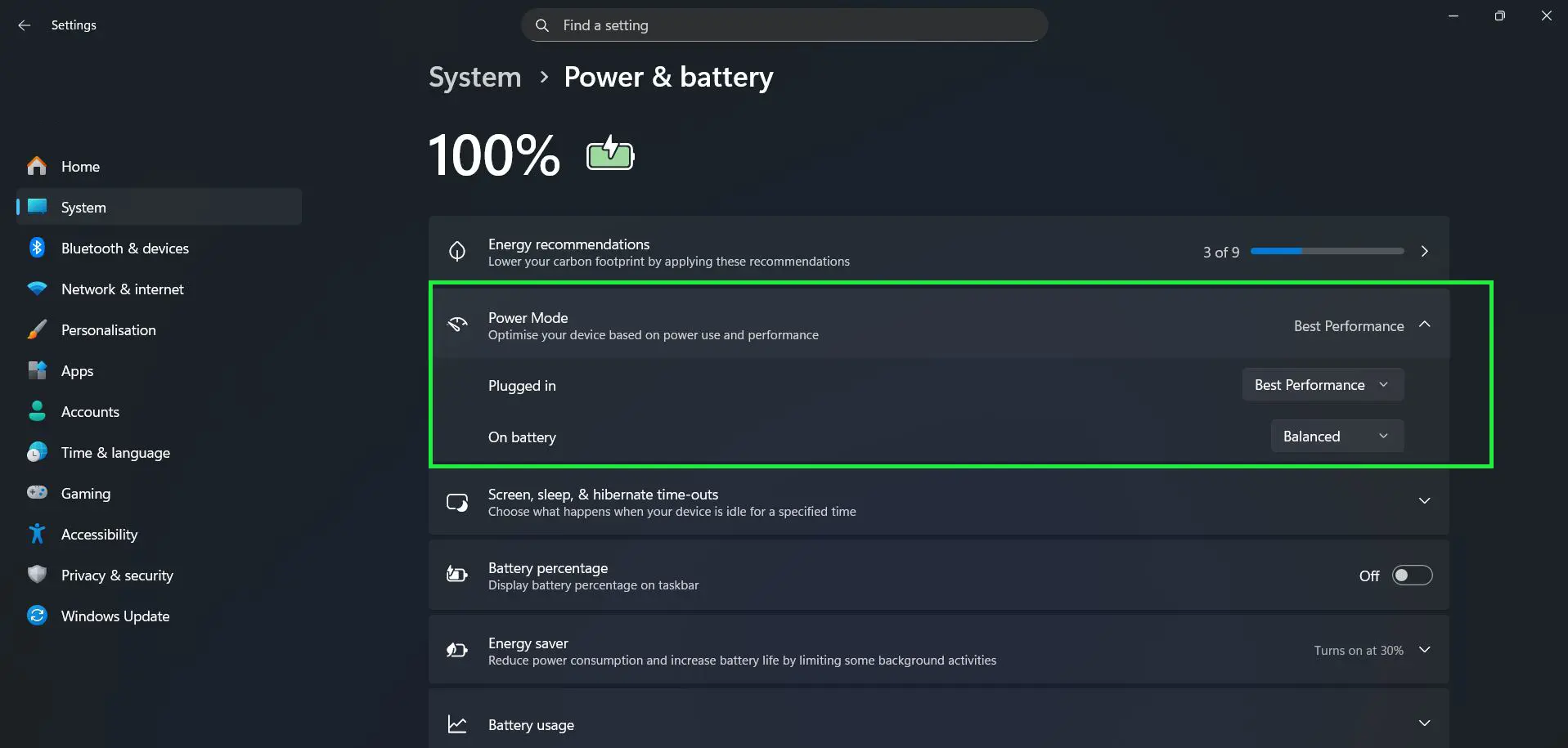
Windows 11 offers different power modes including Best Performance, which maximizes processing power for demanding tasks. Each mode adjusts processor speed, screen brightness, and background activity accordingly. Best Performance increases power consumption and heat generation but provides maximum computing power for gaming, video editing, or other intensive applications.
Energy Recommendations Feature
Windows 11 includes an Energy recommendations section at the top of the Power & battery page. This feature analyzes current settings and suggests changes to reduce carbon footprint. The indicator shows ‘3 of 9’ recommendations applied, with a progress bar displaying how many suggestions have been implemented.
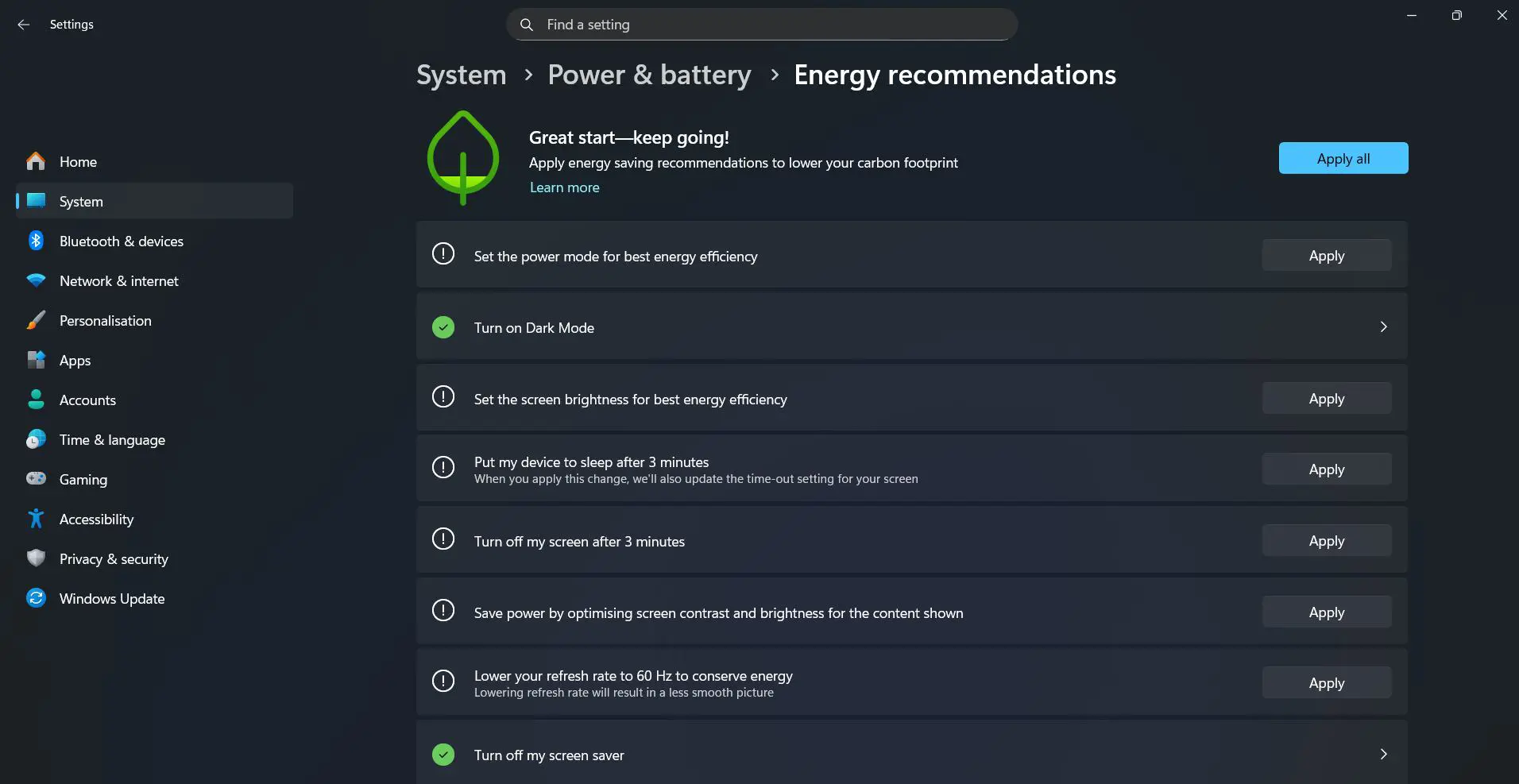
Clicking on Energy recommendations reveals specific suggestions like adjusting screen timeout, enabling dark mode, or modifying sleep settings. The description ‘Lower your carbon footprint by applying these recommendations’ emphasizes environmental benefits alongside energy savings.
Advanced Power Settings Configuration
For more detailed control, Windows 11 retains the classic power options interface. Access this by scrolling down in the Power & battery page to find additional settings:
- Scroll to the bottom of the Power & battery settings page
- Look for links to additional power-related settings
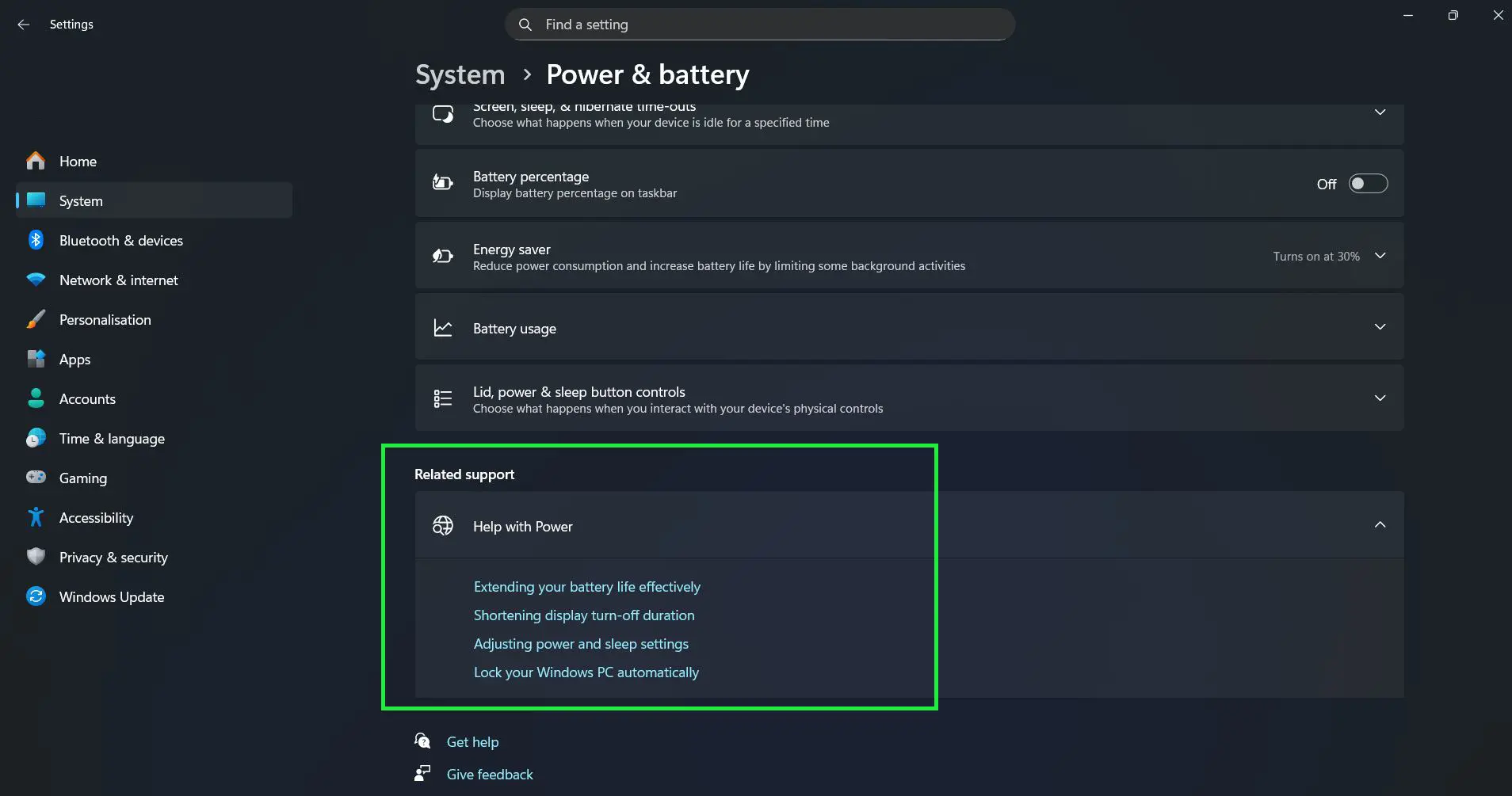
- These may include options for Extending your battery life effectively, Shortening display turn-off duration, and Lock your Windows PC automatically
Advanced settings provide precise control for users who need specific configurations for work or gaming scenarios. Options include processor power management, display brightness levels, and USB selective suspend settings.
Disabling Sleep Mode Completely
Some situations require preventing sleep altogether. Server systems, download stations, or computers running continuous processes need to stay awake:
- Access the ‘Screen, sleep, & hibernate time-outs’ settings in the Power & battery section
- Click the dropdown menu for ‘Make my device sleep after’ under both ‘Plugged in’ and ‘On battery’
- Scroll down in the dropdown menu and select ‘Never’
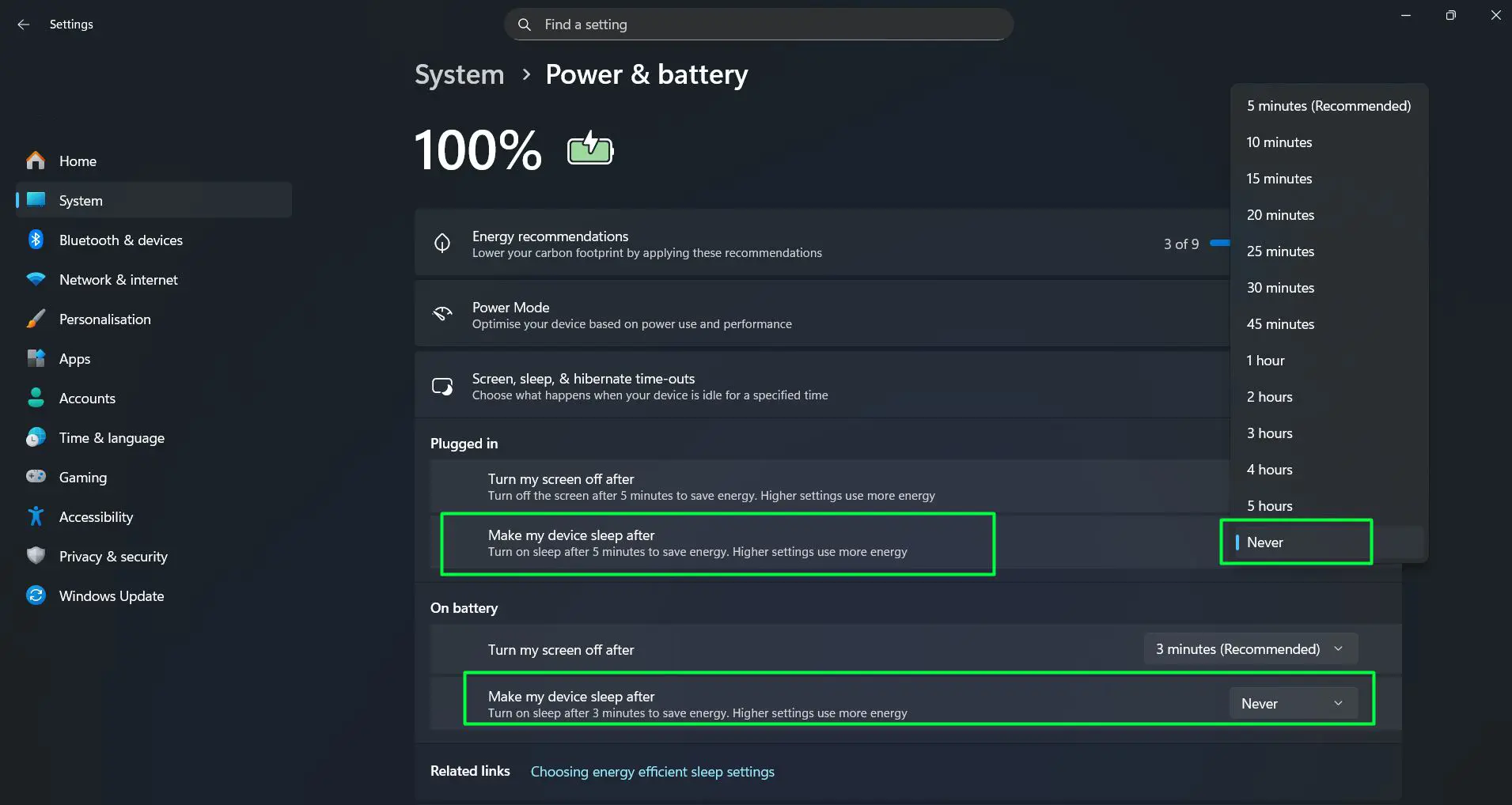
- Confirm the changes by closing the Settings window
Remember that disabling sleep increases power consumption and may cause the system to run hotter over extended periods. Ensure adequate cooling and ventilation when running 24/7.
Pro-Tip: Even when sleep is set to ‘Never’, the screen can still turn off independently. This allows saving power on the display while keeping the computer fully active for background tasks like downloads, uploads, or server operations.
Using Command Prompt for Power Settings
Power settings can also be modified through Command Prompt or PowerShell for quick adjustments:
- Right-click the Start button and select ‘Terminal’ or ‘Command Prompt’
- Type ‘powercfg /change monitor-timeout-ac 30’ to set plugged-in screen timeout to 30 minutes
- Type ‘powercfg /change monitor-timeout-dc 3’ to set battery screen timeout to 3 minutes
- Type ‘powercfg /change standby-timeout-ac 30’ to set plugged-in sleep to 30 minutes
- Type ‘powercfg /change standby-timeout-dc 3’ to set battery sleep to 3 minutes
These commands provide a faster way to adjust settings, especially for IT professionals managing multiple systems. The numbering represents minutes, and setting any value to 0 disables that timer entirely.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between sleep and hibernate in Windows 11?
Sleep keeps RAM powered and allows quick resume within seconds, while hibernate saves RAM contents to the hard drive and completely powers off the system. Hibernate uses no power but takes longer to resume. Sleep is ideal for short breaks, whereas hibernate suits longer periods of inactivity or when preserving battery is critical.
Why does my computer keep waking from sleep on its own?
Network adapters, keyboards, mice, and scheduled tasks commonly cause unexpected wake events. Check Device Manager’s Power Management tab for each device and disable wake permissions for non-essential hardware. Use ‘powercfg /lastwake’ in Command Prompt to identify what last woke the system.
Can power settings affect gaming performance in Windows 11?
Yes, power settings directly impact CPU and GPU performance. The ‘Best performance’ power mode maximizes processing power, which benefits gaming and demanding applications. However, this setting increases power consumption and heat generation compared to balanced or energy-saving modes.
How do I prevent Windows 11 from sleeping during downloads?
Set sleep to ‘Never’ temporarily through Power & battery settings under the ‘Screen, sleep, & hibernate time-outs’ section. Change both the screen and sleep timeouts to ‘Never’ while downloads are in progress. Remember to restore previous settings afterward to maintain energy efficiency.
Will changing power settings damage my laptop battery?
No, adjusting power and sleep settings won’t damage the battery. However, keeping the laptop plugged in 24/7 at 100% charge can reduce battery lifespan over time. Modern Windows 11 laptops include battery protection features that optimize charging patterns when always connected to power.
How do I reset power settings to Windows 11 defaults?
Open Command Prompt as administrator and type ‘powercfg -restoredefaultschemes’. This command resets all power plans to factory settings. Alternatively, manually adjust the settings back to the recommended values shown in the Power & battery settings page, typically 3 minutes for battery mode.
Where is the hibernate option in Windows 11 power settings?
Hibernate settings appear in the ‘Screen, sleep, & hibernate time-outs’ section of Power & battery settings. If hibernate options aren’t visible, the feature may be disabled. Enable it through Command Prompt by typing ‘powercfg /hibernate on’ as administrator, then restart Settings to see the option.
Why don’t my power settings save after changing them?
Group Policy settings or administrative restrictions might override personal preferences in managed environments. Contact the IT department if working on a company computer. On personal systems, running the Settings app as administrator or checking for pending Windows updates often resolves saving issues.
